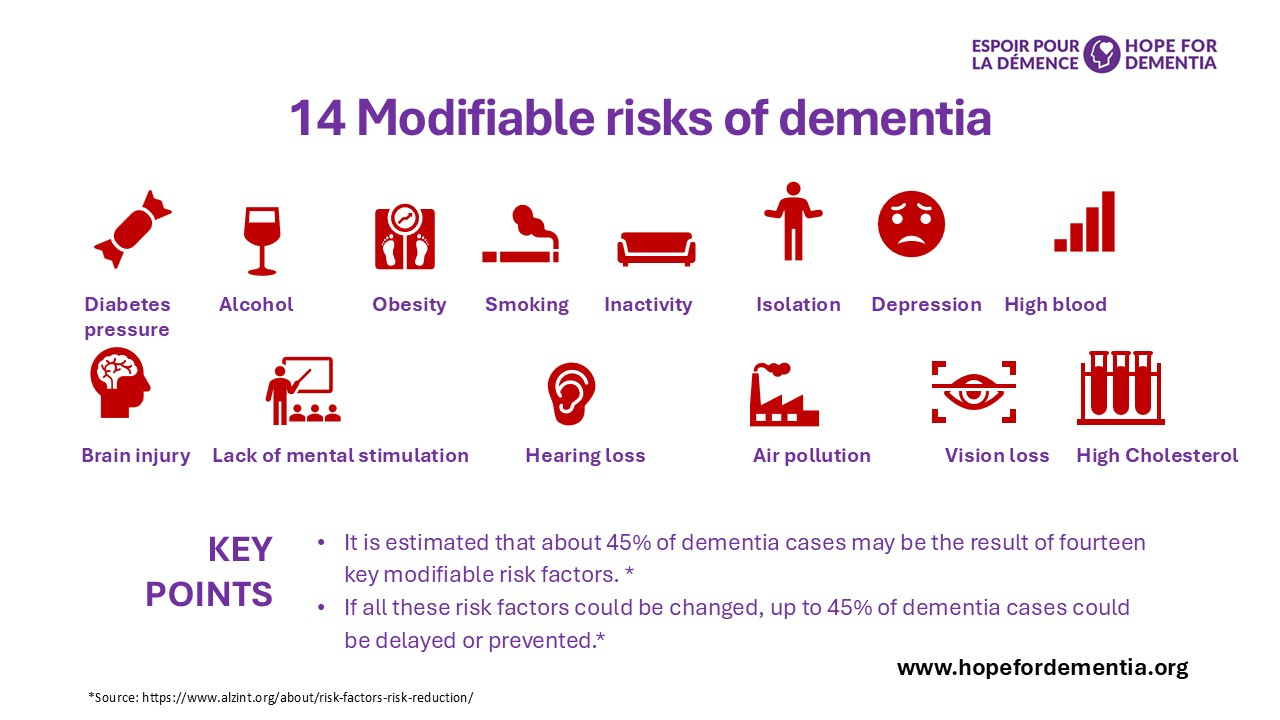
Aging and genetics are two known risk factors of developing dementia. Although aging and genetics cannot be prevented, a growing body of research evidence exists that identifies 14 potentially modifiable risk factors.
Physical inactivity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, air pollution, head injury, infrequent social contact, less education, obesity, hypertension, diabetes, depression, hearing impairment, vision loss and high cholesterol are the 14 modifiable risk factors. Recent research indicates that if all of these risk factors could be modified, up to 45% of cases of dementia could be delayed or prevented.
Reduce the risks of dementia
- Risk factors are aspects of your lifestyle, environment or genetics that make disease more likely.
- Risk factors alone do not cause a disease, but they increase the chances of developing the disease.
- Even without the 14 modifiable risk factors, a person can still be diagnosed with dementia.
Some risk factors are modifiable, and others are not.
Risk factors that cannot be modified are – age, gender and genetics.
- After age 65, the chance of developing dementia increases, doubling approximately every five years.
- Women are more likely to develop dementia. The cause is still being researched.
- Two to 5 percent of dementia cases have been linked to genetics.
Taking action – e.g. physical exercise, healthy nutrition and social interaction – can reduce the risks and can potentially prevent dementia or significantly delay a dementia diagnosis.